Prerequisites
This series will cover how to create K2 nodes in C++ for Unreal Engine 5.
Before proceeding, this series will assume a solid foundation in C++ and good knowledge of the Unreal Engine C++ framework.
History
Kismet is a node based visual scripting system. It was introduced with Unreal Engine 3 in 2006 and a new version (shortened to K2) was released with Unreal Engine 4 in 2014. The new version, K2, is the focus of this series.
What are K2 nodes?
K2 nodes are the foundation of “Blueprints” in Unreal Engine 4 and 5. Any node that you can add into a Blueprint graph has a K2 node behind it written in C++. Other graph editors have their own respective nodes, such as Control Rig, Niagara, and MetaSounds, however K2 are specific to Blueprints.
The simplest K2 node is probably the “Reroute” node.
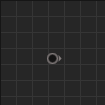
The code behind this is dead simple as its purpose is purely cosmetic.
// Copyright Epic Games, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
class UK2Node_Knot : public UK2Node
{
GENERATED_UCLASS_BODY()
public:
virtual void AllocateDefaultPins() override;
virtual void ExpandNode(class FKismetCompilerContext& CompilerContext, UEdGraph* SourceGraph) override;
...
};Even though this is the simplest K2 node, it still overrides over a dozen functions from UK2Node and UEdGraphNode (which are the main parent classes for custom nodes). I’m going to focus on AllocateDefaultPins and ExpandNode as these are the bread and butter of K2 nodes; most other functions control how your node looks and behaves in the graph.
AllocateDefaultPins
As the name suggests, AllocateDefaultPins is responsible for creating input and output pins for the class. This function is called whenever ReconstructNode is called, which is usually whenever state in the node is changed and pins need to be recreated.
A good example of such state changes are when pins for structs are split/recombined.
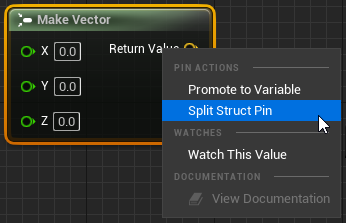
When these pins are split/recombined, the split state is set and the node is reconstructed. This causes AllocateDefaultPins to be called which reads the node state and creates additional pins if needed.
ExpandNode
ExpandNode is the function that will make you question your own sanity. It’s called whenever you compile the blueprint and is responsible for taking your single node entity in the node graph and expanding it to any intermediate nodes, such as function calls and custom events. It also does pin rewriring needed for those intermediate nodes.
A great example of node expansion is timelines. The single Timeline node is expanded into a function call and 2 custom events.
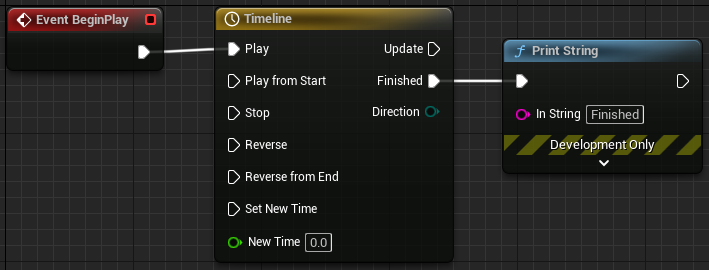
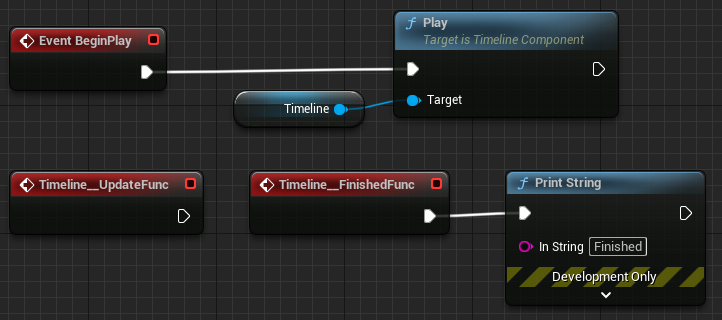
For more complex nodes, the implementation of ExpandNode will eclipse the rest of the class and can be an absolute pain to diagnose and debug. Ask me how I know.
What next?
K2 nodes are a great skill to have, however it’s extra code to maintain and their application is relatively limited because there is usually an easier way, such as Blueprint Function Libraries and Blueprint Macros.
Special thanks to Daekesh for taking the time to proof this article.
The next article in this series will cover how to create a bog standard K2 node.